Introduction
Skin pigmentation, a critical aspect of human biology, plays a significant role in our appearance and health. The article "Skin Pigmentation Types, Causes and Treatment—A Review" by Amin Mahmood Thawabteh et al., provides a comprehensive insight into this fascinating subject. This blog post aims to distill the key points from the article, shedding light on the types of skin pigmentation, their causes, and available treatments.
The Science of Skin Pigmentation
Skin pigmentation refers to the color of our skin, primarily determined by melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes in the epidermal layer. There are two main types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin, responsible for darker skin tones, offers protection against UV radiation and skin cancer. In contrast, pheomelanin, which leads to lighter skin tones, reflects heat but provides less UV protection.

Factors Influencing Skin Pigmentation
The variability in skin pigmentation is influenced by several factors:
1. Genetics: Our genetic makeup plays a pivotal role in determining skin color. It influences the number of melanocytes and the type of melanin produced.
2. Sun Exposure: UV radiation from the sun stimulates melanin production, leading to tanning or, in some cases, hyperpigmentation.
3. Medications: Certain drugs can affect melanin synthesis, altering skin pigmentation.
Pigmentation Disorders
- Albinism: A genetic condition characterized by a lack of melanin, resulting in very light skin, hair, and eyes.
- Melasma: Often hormonal, this condition causes brown or gray patches, primarily on the face.
- Vitiligo: An autoimmune disorder where the skin loses pigment in patches.
- Addison’s Disease: A hormonal disorder that can lead to increased pigmentation.
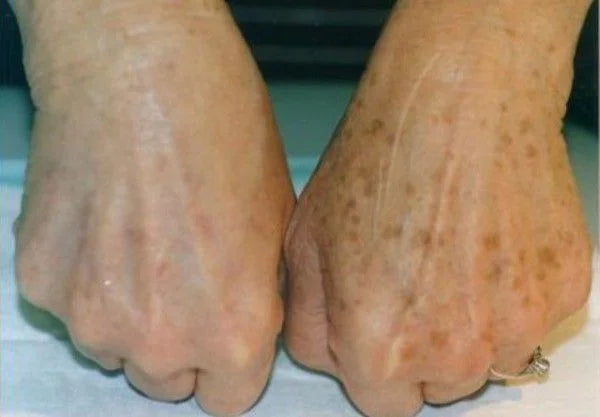
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin following an inflammatory skin condition like acne.
Treatment Options

Treatment for pigmentation disorders varies based on the condition and its severity. The main approaches include:
1. Topical Treatments: These include creams and ointments containing ingredients like hydroquinone, corticosteroids, and retinoids, which help in lightening hyperpigmented areas.
2. Oral Medications: Certain oral drugs can be effective in treating pigmentation disorders. For instance, tranexamic acid is used for melasma, and isotretinoin is prescribed for severe acne.
3. Cosmetic Procedures: Procedures like chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can be effective in treating certain pigmentation disorders.
4. Herbal Remedies: Some herbal ingredients are known to have skin-lightening properties and are used in various cosmetic products.
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing skin pigmentation disorders involves:
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can prevent pigmentation changes due to sun exposure.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and avoiding skin irritants can help maintain normal skin pigmentation.
- Regular Skin Checks: Monitoring skin changes and consulting a dermatologist for any concerns is crucial.

Conclusion
Understanding skin pigmentation is essential for both aesthetic and health reasons. While variations in skin color are a natural and beautiful aspect of human diversity, disorders in pigmentation can sometimes indicate underlying health issues. With advancements in dermatology, various treatments are available to manage and treat pigmentation disorders effectively. However, prevention, primarily through sun protection and a healthy lifestyle, remains key.